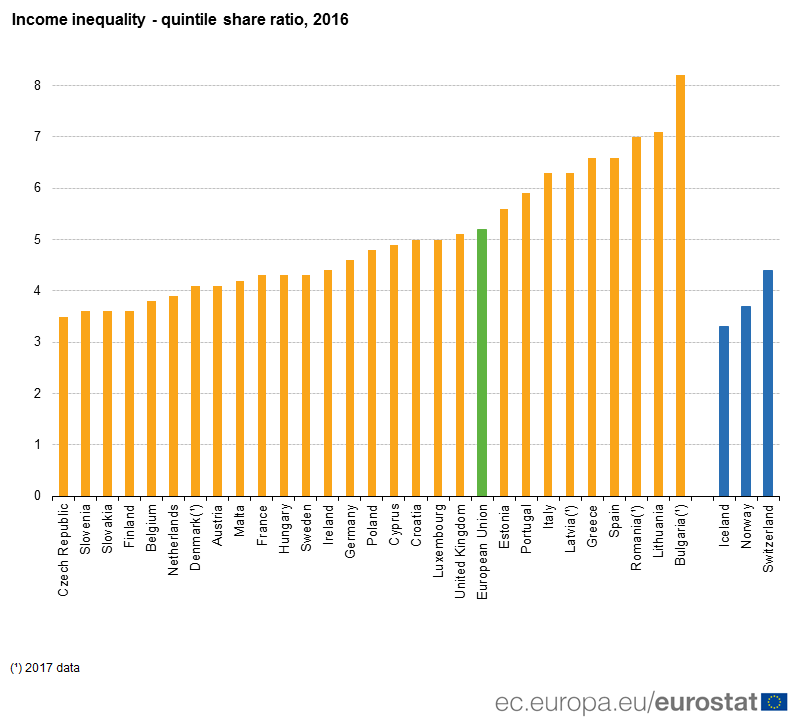
Eurostat data on income inequalities has revealed a varying picture across central and eastern Europe, with the Balkan states of Serbia and Bulgaria showing significantly higher rates of inequality than most former-Communist nations.
“The quintile share ratio is the proportion of the total equivalised disposable income received by the 20 per cent of the population with the highest income (top quintile) to that received by the 20 per cent of the population with the lowest income (lowest quintile),” explains the Eurostat report.
The reports reveals that the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Slovenia and Slovakia have similar levels of income inequality, while Bulgaria has seen the highest increase of any EU state, going up 0.3 between 2016 and 2017. Serbia’s income inequality increased from 9.0 to 9.7.
The statistics also revealed that Estonia had the largest decrease in income inequality in EU states between 2016-2017, from 6.2 to 5.6, with Lithuania closely following at 7.5 to 7.1.
The Czech Republic has maintained its score of 3.5 from 2015 and 2016, holding its position as the state with the most equal distribution of income in the European Union.
However, the report states the data “fails to provide information in relation to non-monetary factors that may play a significant role in determining the quality of life of a particular population.”
Throughout the EU, the top 20 per cent of the population (with the highest income) received 5.2 times as much income as the bottom 20 per cent.